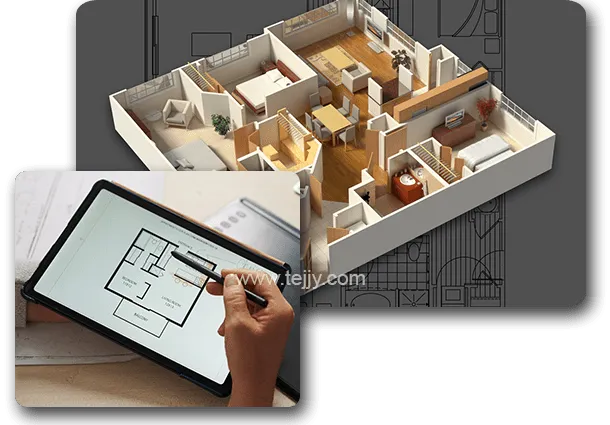
In today’s rapidly advancing world of technology, designing planning 3D renderings have become integral in various industries, particularly in architecture, interior design, real estate, and product design. The ability to visualize a project before its physical creation offers numerous advantages, such as enhanced communication, fewer errors, and the ability to tweak designs without the costs of physical alterations. This article will explore the crucial role that designing and planning play in the 3D rendering process, and how they contribute to the success of modern projects.
1. Understanding 3D Renderings: What Are They?
Before diving into the specifics of designing and planning for 3D renderings, it’s important to understand what 3D renderings are. Essentially, 3D renderings are computer-generated images (CGIs) that create realistic or stylized visualizations of projects, objects, or spaces. They are a result of 3D modeling, a process in which a designer creates a three-dimensional representation of a design in a software application. Once this model is created, it can be rendered into an image or animation, showing how the design will look in the real world.
In the context of designing planning 3D renderings, these visuals play a critical role in communicating the vision for a project. Whether it’s a building, a product prototype, or an interior space, 3D renderings allow stakeholders to visualize the final product before any actual construction or production takes place. This helps everyone involved in the project — from clients and architects to engineers and contractors — understand what is being created and ensure that the design meets their expectations.
2. The Role of Designing in 3D Renderings
Designing is the foundation of any 3D rendering process. It involves the creative and technical aspects of how the final product will look and function. In the case of architectural projects, the design process will consider everything from the building’s exterior appearance to the materials used, as well as how the structure fits within its environment.
a. Conceptualizing Ideas
Effective designing planning 3D renderings begins with a strong design concept. This initial phase is where ideas are generated and refined. Designers often start by sketching rough concepts or mood boards that capture the intended aesthetic and functional goals of the project. With 3D software, these early-stage ideas can be turned into more realistic, interactive models that can be modified and reviewed. The ability to quickly visualize different iterations and concepts gives designers more flexibility to explore new possibilities.
For example, in the case of a residential home, a designer may start with basic sketches of the structure. The 3D model can then be adjusted to experiment with different roof styles, window placements, and interior layouts. This process helps to solidify ideas and identify potential issues early in the project, before any physical construction begins.
b. Detailed Design and Refinement
Once the concept is established, the design process becomes more detailed. At this stage, designing planning 3D renderings come into play to ensure the project is both visually appealing and functional. Designers will add materials, textures, and lighting effects to the model, simulating how the final product will look under real-world conditions. This step is crucial for refining the details and making decisions about color schemes, surface finishes, and other key elements.
The ability to make these adjustments virtually in 3D software saves time and reduces the risk of costly mistakes. For instance, an architect can experiment with different material textures to see how they look in the 3D rendering, avoiding the need for expensive samples or prototypes. Additionally, interior designers can experiment with lighting schemes to determine how different light sources will affect the mood of a space.
c. Collaboration and Communication
Effective designing planning 3D renderings enable seamless collaboration and communication between various stakeholders. In modern projects, designers often work in teams with engineers, contractors, and clients. 3D renderings allow everyone involved to see a visual representation of the project, ensuring that everyone is on the same page.
For instance, in a large commercial construction project, the architectural design team may be working alongside structural engineers and contractors. Through shared 3D models, everyone can see how their individual components fit into the overall design, which helps prevent issues that could arise from miscommunication. Moreover, clients can provide feedback on the design through interactive 3D models, making it easier to incorporate changes before moving forward with construction.
3. The Importance of Planning in 3D Renderings
Planning is an essential step in the 3D rendering process. While designing focuses on creativity and conceptualization, planning ensures that the design is executable and aligns with the project’s goals, budget, and timeline. Good planning helps to streamline the rendering process and prevents delays, ensuring that the project is completed on schedule and within budget.
a. Understanding Project Requirements
A well-structured designing planning 3D renderings process begins with a thorough understanding of the project’s requirements. This includes budget constraints, regulatory requirements, client preferences, and any technical limitations. For example, a commercial real estate project may need to meet specific zoning and building codes, which must be considered during the planning phase.
Understanding these requirements allows designers to tailor the 3D renderings to meet all necessary guidelines and ensure that the design is feasible. Furthermore, planning helps identify any potential challenges or obstacles that could arise during the project’s execution. For instance, if a building is being designed in an area with a high water table, the planning phase can highlight the need for special structural considerations.
b. Timeline and Resource Allocation
Planning also involves determining the timeline for completing the project and allocating resources effectively. For designing planning 3D renderings, this means establishing a clear schedule for each phase of the project, from conceptualization to the final rendered images or animations. The more detailed and realistic the 3D renderings need to be, the more time and effort are required.
Additionally, effective planning ensures that the right tools and resources are available to the design team. This may include access to advanced 3D rendering software, specialized hardware, or skilled professionals who can execute the renderings at the highest quality. Proper resource allocation can prevent delays and ensure that the project stays on track.
c. Identifying and Addressing Potential Issues
Another important aspect of planning is identifying potential issues early on. With 3D renderings, designers and planners can foresee problems before they arise, whether it’s an issue with structural integrity, design flaws, or aesthetic concerns. Early identification allows for adjustments to be made before any work begins, preventing costly changes down the line.
For instance, if a designer notices that the layout of a room doesn’t flow as intended in the 3D rendering, they can easily tweak the design and test it again. This flexibility is invaluable in ensuring that the final product meets the expectations of all stakeholders.
4. How Designing and Planning Work Together in 3D Renderings
The process of designing planning 3D renderings is a dynamic, iterative cycle in which both design and planning are constantly evolving. While the designer works on refining the creative aspects of the project, the planner ensures that the design aligns with the practical requirements of the project. Both elements must work in tandem to ensure the success of the project.
For instance, the initial design phase may involve brainstorming ideas and creating basic renderings. As the project progresses, planning steps are introduced, ensuring that each design element fits within the constraints of the budget and timeline. The design can then be adjusted based on the feedback received during the planning phase, resulting in a more refined and executable solution.
5. The Future of Designing and Planning in 3D Renderings
As technology continues to advance, designing planning 3D renderings are likely to become even more sophisticated. The use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) is already making it possible for designers and clients to interact with 3D models in real time. This technology will allow for even more immersive experiences, where stakeholders can walk through a virtual representation of a project and provide immediate feedback.
Additionally, AI and machine learning may play an increasingly important role in the design and planning process, helping to optimize the creation of 3D renderings based on user preferences and project specifications.
Conclusion
The role of designing planning 3D renderings in modern projects cannot be overstated. By allowing designers, planners, and clients to visualize a project before it comes to life, 3D renderings provide a powerful tool for enhancing communication, refining designs, and preventing errors. By carefully balancing the creative aspects of designing with the practical considerations of planning, these renderings ensure that modern projects are both aesthetically pleasing and functional, ultimately leading to the successful realization of the original vision.
Also Read
- ► Master Content Development Strategies for Effective Growth
- ► How to Ensure the Quality of Masonry Work for Your Project
- ► Why the Essentials Hoodie is a Must Have for Every Wardrobe
- ► Why Are Roman Blinds a Great Choice for Privacy and Style?
- ► The Red Hellstar Hoodie A Bold Fashion Statement with a Touch of Edgy Style
- ► essentials hoodie canada Styling Tips for Every Season
- ► The Ultimate Guide to Stussy Hoodies: Style Meets Comfort
- ► The Timeless Appeal of Bape Hoodies: A Streetwear Icon
- ► The Ultimate Guide to Rod Wave Hoodies: A Must-Have for Fans
- ► Transform Your Well-being with Virtual Therapy Sessions
- ► Corteiz Cargos The Epitome of Streetwear Cool
- ► Discover the Comfort and Style of Essentials Clothing
- ► Finding Happiness and Fulfillment After a Breakup
- ► Essentials Jacket A Blend of Style and Functionality
- ► The Spider Jacket Where Function Meets Fashion