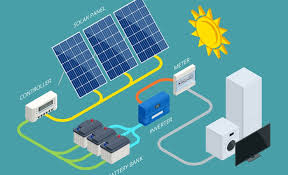
Solar Power Solutions
In recent years, the global demand for sustainable energy solutions has grown significantly, and solar power has emerged as one of the most popular and accessible forms of renewable energy. Solar power solutions harness the energy from the sun to generate electricity, offering a cleaner, greener alternative to conventional energy sources like coal and natural gas. With increasing concerns about climate change, rising energy costs, and the need for energy independence, solar power has become an essential solution for both residential and commercial applications. In this article, we will explore what solar power solutions are, how they work, their benefits, and the different types of solar systems available.
What Are Solar Power Solutions?
Solar power solutions refer to the technology and systems that capture and convert sunlight into electricity. These systems typically consist of solar panels, an inverter, a battery (in some cases), and a mounting structure. Solar panels, made of photovoltaic (PV) cells, are the core component of any solar power solution. They absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The inverter then converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used to power homes, businesses, and other electrical systems.
Solar power solutions can be used to meet all or part of a building’s energy needs, depending on the system size and location. They can be installed on rooftops, ground-mounted structures, or integrated into building materials such as solar windows and solar roofing tiles. With advancements in solar technology, solar power has become a viable option for reducing energy bills, promoting sustainability, and increasing energy independence.
How Do Solar Power Solutions Work?
Solar power solutions work by capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the process works:
- Sunlight Absorption: Solar panels, made up of photovoltaic cells, absorb sunlight during the day. These cells are made from semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that absorb photons from the sun.
- Electricity Generation: When sunlight hits the photovoltaic cells, it excites the electrons in the material, generating direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity is not suitable for household appliances, which require alternating current (AC) electricity.
- Inverter Conversion: The DC electricity produced by the solar panels is sent to an inverter. The inverter converts DC electricity into AC electricity, making it suitable for household use.
- Power Distribution: Once the electricity is converted into AC power, it is distributed throughout the home or building to power appliances, lights, heating, and cooling systems.
- Excess Energy Storage or Grid Connection: If the solar power system generates more electricity than the building needs, the excess energy can be stored in batteries for later use, or it can be fed back into the grid through a net metering system. In net metering, the excess electricity generated by the solar panels is sent to the local utility grid, and the building owner receives credits for the energy supplied.
Benefits of Solar Power Solutions
Solar power solutions offer a wide range of benefits, making them an attractive option for homeowners, businesses, and governments worldwide. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Environmental Impact
One of the most significant advantages of solar power is its minimal environmental impact. Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that does not produce harmful greenhouse gases or other pollutants. By using solar power, individuals and businesses can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to the fight against climate change. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power does not rely on burning resources, meaning it has a much lower impact on the environment.
2. Cost Savings
Solar power solutions can significantly reduce energy bills. Once installed, solar panels generate free electricity from the sun, reducing the need to purchase electricity from the grid. This can lead to substantial savings over time, especially in areas with high electricity rates. Additionally, many governments offer incentives, rebates, and tax credits to help offset the cost of installation, making solar power more affordable for homeowners and businesses.
3. Energy Independence
By investing in solar power solutions, individuals and businesses can reduce their reliance on the utility grid. This is especially important in regions where energy prices are volatile or where power outages are common. Solar power allows for greater energy independence, ensuring a reliable source of electricity even during periods of high demand or natural disasters.
4. Low Maintenance
Solar power systems are relatively low maintenance. Once installed, solar panels require minimal upkeep to continue functioning efficiently. Regular cleaning and occasional inspections are typically all that is needed to maintain optimal performance. Solar power systems can last for decades, with many manufacturers offering warranties of 20 to 25 years.
5. Job Creation
The growing demand for solar power solutions has created numerous job opportunities in the renewable energy sector. From manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research, the solar industry has become a significant source of employment worldwide. As more people transition to solar energy, the number of jobs in the sector is expected to continue to rise.
Types of Solar Power Solutions
There are several different types of solar power systems, each designed to meet specific energy needs and installation requirements. Here are the most common types of solar power solutions:
1. Grid-Tied Solar Systems
Grid-tied solar systems are the most common type of solar power system. These systems are connected to the local utility grid and allow homeowners and businesses to use solar energy while still being connected to the grid for backup power when necessary. Any excess energy generated by the system is sent to the grid, and the owner receives credits for the energy supplied.
- Pros: Lower initial investment due to no need for batteries. Net metering can provide credit for excess energy.
- Cons: No backup power during grid outages unless a battery system is added.
2. Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar systems are designed for locations that are not connected to the utility grid. These systems require batteries to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy periods. Off-grid solar systems are ideal for remote locations or properties where connecting to the grid is not feasible.
- Pros: Complete energy independence from the grid.
- Cons: Higher upfront costs due to the need for batteries and additional equipment.
3. Hybrid Solar Systems
Hybrid solar systems combine both grid-tied and off-grid features. These systems are connected to the grid, but they also include a battery storage system to store excess energy. In the event of a power outage, the battery can supply electricity, providing backup power without the need for a generator.
- Pros: Energy independence with backup power and the ability to send excess energy to the grid.
- Cons: Higher installation costs due to the inclusion of battery storage.
4. Solar Water Heating Systems
Solar water heating systems use solar energy to heat water for domestic or commercial use. These systems typically consist of solar collectors, a storage tank, and a circulation system. Solar water heaters are an efficient way to reduce energy consumption for hot water needs, especially in sunny climates.
- Pros: Reduces energy costs for heating water.
- Cons: Limited to water heating applications.
Conclusion
Solar power solutions offer a sustainable and cost-effective way to generate clean energy while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. With a variety of system types available, including grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid systems, solar power can meet the energy needs of residential, commercial, and industrial applications. By harnessing the power of the sun, individuals and businesses can reduce their carbon footprint, save on energy costs, and increase their energy independence. As solar technology continues to evolve, the future of solar power solutions looks brighter than ever, offering a path to a more sustainable and energy-efficient world.
Also Read
- ► Bed Bug Spray: The Ultimate Solution for Bed Bug Infestation
- ► How to Clean a Leather Bag Without Damaging It? Beginner’s Guide
- ► Online Cricket ID – Top Tips and Strategies at Virat777
- ► Ensuring Quality Healthcare with Multispeciality Hospital Services
- ► Cockroach Killer: An Effective Solution for Eradicating Roaches
- ► Viscose Staple Fibre Price Trends: Market Insights, Forecasts, and Analysis
- ► How to Maintain Your Market Tarpaulin for Long-Term Use
- ► Innovative Uses of Tarpaulins in Modern Marketplaces
- ► How to Choose the Best Places to Buy Essentials Shorts
- ► Budget-Friendly Tarpaulins for New Market Vendors
- ► Siemens Hearing Aids: A Comprehensive Guide to Innovation and Quality
- ► Nambiar District 25: Elevating Modern Living in Bangalore
- ► Premium Quality Washroom Cubicles for Businesses
- ► Sobha Ayana Reclassifying Extravagance Living in Bangalore
- ► Price of Hearing Aids: What to Expect and Factors That Influence Cost