Introduction
Prefilled syringes have become increasingly important in modern healthcare, providing convenience, accuracy, and safety to both healthcare providers and patients. Used for administering a wide range of medications, these preloaded devices are designed to simplify and improve the process of medication delivery. This article explores the types of prefilled syringes, their uses across various medical fields, and the numerous advantages they offer.
Definition
A prefilled syringe is a medical device preloaded with a single, exact dose of medication by the manufacturer, designed to simplify and enhance the accuracy of drug administration. Unlike traditional syringes, which require manual loading from a vial, prefilled syringes come ready-to-use, reducing preparation time and minimizing the risk of dosage errors and contamination. Widely used for vaccines, emergency medications, and chronic disease treatments, prefilled syringes offer convenience, safety, and efficiency in various healthcare settings.
Understanding Prefilled Syringes
A prefilled syringe is a single-dose packet of medication to which a needle has been fixed by the manufacturer. Unlike traditional syringes, which require manual loading of medication, prefilled syringes come ready-to-use, significantly reducing the likelihood of dosing errors and contamination. These devices have quickly gained favor in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly as injectable medications become more common.
Types of Prefilled Syringes
Prefilled syringes vary in their materials, applications, and usability features. The main types are broken down as follows:
Glass Prefilled Syringes:
- Glass syringes are the traditional choice for prefilled syringes and remain widely used due to their chemical stability and low interaction with drug compounds. They effectively preserve the integrity of delicate pharmaceuticals.
- However, glass syringes are more prone to breakage, which can pose challenges in high-paced clinical environments. Despite this drawback, they are well-suited for medications that require minimal contamination risk, such as vaccines and biologics.
Plastic Prefilled Syringes:
- In recent years, plastic syringes made from cyclic olefin polymer (COP) or cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) have gained popularity. These materials are lighter and shatter-resistant, making them safer in various settings.
- Plastic syringes are suitable for medications that don’t interact with the materials, though some drugs may require glass syringes to avoid possible degradation. Plastic syringes are commonly used for emergency medications and in locations with high patient turnover.
Dual-Chamber Prefilled Syringes:
- Dual-chamber syringes are designed to hold two different solutions, typically a lyophilized (freeze-dried) drug and a liquid diluent. When ready to administer, the two chambers are mixed, enabling immediate preparation of the medication.
- These syringes are used mainly for sensitive drugs that must be mixed immediately before administration, such as some biologicals or vaccines that require reconstitution.
Safety-Engineered Prefilled Syringes:
- Safety-engineered syringes come with features like retractable needles or safety caps to reduce the risk of accidental needle sticks. These are particularly valuable in hospital settings where needle injuries can lead to cross-contamination.
- Safety syringes are often mandatory for high-risk medications or in high-traffic settings, ensuring the protection of healthcare providers.
Uses of Prefilled Syringes
Prefilled syringes have versatile applications across healthcare sectors, ranging from chronic disease management to emergency care. Some of the most common applications include:
Vaccinations:
Prefilled syringes are extensively used in vaccine administration, from annual flu shots to COVID-19 vaccinations. They ensure accurate dosage, which is critical in vaccine efficacy and minimizes waste during mass immunization efforts.
Anticoagulants and Blood Thinners:
Medications like heparin, used for preventing blood clots, are often delivered in prefilled syringes. These syringes facilitate fast, precise administration, which is vital in preventing and managing thrombotic events.
Chronic Disease Management:
Patients with chronic diseases, such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, often require regular injections. Prefilled syringes allow for easy self-administration, reducing dependence on healthcare facilities and promoting patient independence.
Emergency Medications:
Certain emergency drugs, like epinephrine for anaphylactic reactions, are prefilled for rapid use. These syringes allow healthcare providers and even patients to quickly administer life-saving drugs in critical situations.
Biologics and Specialty Pharmaceuticals:
Biologics, which are more complex than traditional drugs, often need prefilled syringes to ensure precise dosing. These medications are crucial in treating autoimmune diseases, cancer, and other conditions requiring high-value therapeutics.
Advantages of Prefilled Syringes
The adoption of prefilled syringes has transformed healthcare, with benefits extending to patients, healthcare providers, and pharmaceutical companies. Here are some of the primary advantages:
Improved Accuracy and Precision:
One of the significant benefits of prefilled syringes is the accuracy of the dosage. As the syringes are preloaded with an exact dose by the manufacturer, the risk of human error during preparation is minimized. This is essential for medications that require precise dosing to avoid under- or overdosing.
Enhanced Safety and Reduced Contamination:
Prefilled syringes are sealed and sterile, minimizing the risk of contamination. In contrast, traditional syringes, which require drawing medication from a vial, expose the drug to potential contaminants during preparation. In hospital settings, this feature reduces the likelihood of infections or other complications.
Convenience and Efficiency:
Prefilled syringes save time, particularly in emergency situations. Since they come ready-to-use, healthcare providers can administer medications more quickly, which can be lifesaving in critical situations. This efficiency is also valuable in high-volume vaccination drives, where speed and accuracy are crucial.
Patient Compliance and Ease of Use:
For patients who self-administer medication, prefilled syringes offer convenience and ease. Patients don’t need to measure doses or handle vials, which can be challenging for those with mobility or vision impairments. Prefilled syringes encourage better adherence to prescribed regimens, especially for chronic conditions requiring regular injections.
Reduced Waste:
In many cases, prefilled syringes help reduce drug wastage, as each syringe contains only the required dose. This is particularly beneficial for high-cost medications, where wastage can lead to significant financial loss. It also simplifies inventory management in clinical settings.
Cost-Effective in the Long Run:
Although prefilled syringes may have a higher initial cost, their benefits often lead to cost savings in the long term. Fewer dosing errors, reduced waste, and minimized contamination risks result in fewer complications and hospital readmissions, ultimately reducing healthcare costs.
Environmentally Friendly:
Prefilled syringes, when manufactured with recyclable materials, have a smaller environmental footprint. They reduce the need for separate vials and syringes, cutting down on plastic waste. Some manufacturers are exploring biodegradable materials, further enhancing the environmental benefits.
Key Considerations and Challenges
While prefilled syringes offer many benefits, there are some challenges to consider. For instance:
Compatibility with Medication:
Some medications may interact with syringe materials, affecting the drug’s stability. Ensuring compatibility between the medication and syringe materials is essential, especially for biologics that are sensitive to environmental factors.
Storage and Transportation:
Prefilled syringes often require specific storage conditions, especially for biologics that need refrigeration. Maintaining the cold chain from manufacturer to end user is critical to preserving the medication’s efficacy, which can be challenging in areas with limited resources.
Cost of Production:
The manufacturing process for prefilled syringes can be more complex than for traditional vials, increasing production costs. For some healthcare facilities or patients, the higher upfront cost may pose a barrier, particularly if the medication is not covered by insurance.
The Future of Prefilled Syringes
Advancements in technology and materials are likely to drive further innovations in prefilled syringe design. Researchers are exploring new materials that improve compatibility with sensitive drugs, as well as smart syringes that can monitor dosing and record patient data. Additionally, as more medications shift from oral to injectable forms, prefilled syringes will play a critical role in ensuring safe and efficient drug delivery.
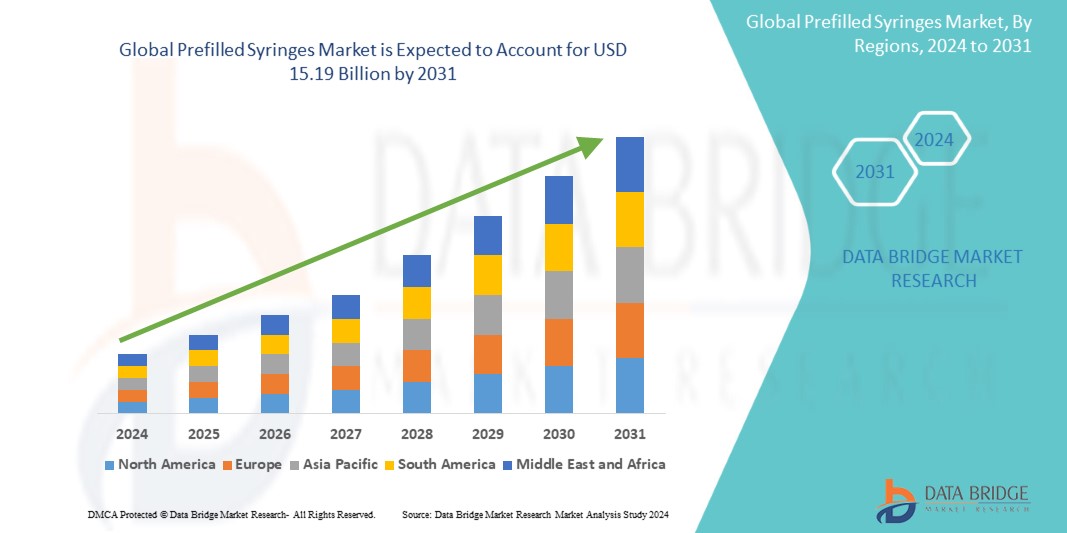
Growth Rate of Prefilled Syringes Market
The size of the global prefilled syringes market was estimated at USD 7.35 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.50% from 2024 to 2031, reaching USD 15.19 billion.
Conclusion
Prefilled syringes have revolutionized medication administration by providing a safer, more efficient, and convenient alternative to traditional syringes. Their advantages—such as improved accuracy, reduced contamination risk, and ease of use—make them a valuable asset in healthcare. As innovations continue to improve their design and accessibility, prefilled syringes are poised to become even more integral to modern medicine, ensuring optimal patient care and adherence across a wide range of medical applications.
Also Read
- ► Buy Trenabol Inj 1 Amp Boost Lean Muscle Strength
- ► Kadali Vivaha in Srirangapatna: A Comprehensive Guide
- ► Use CUET Previous Year Question Paper for Preparation
- ► How to Choose the Best Label Printing Software for Your Business Needs
- ► Top Hospital Management Trends Shaping Healthcare in 2024
- ► Mebendazole for Worms: How It Works and Why It’s Effective
- ► ISO Certification is the Key for Global Quality Standards
- ► International Travel Made Simple with the Right Passport
- ► The Rise of Tracksuits in High-Fashion
- ► Web Agency Dubai: Revolutionizing Web Design in Dubai
- ► Streamline Your Business with Udyam Registration
- ► Securing Your Social Presence: Understanding Instagram Privacy Settings
- ► Web Agency Dubai: Revolutionizing Web Design in Dubai
- ► Udyam Registration – Your Gateway to Government Benefits and Schemes
- ► Honey Stick Packaging: The Sweet Solution to Convenience